Basics Graph Part 1
Basics Graph
A graph is a data structure formed of a set of nodes and vertices. It is commonly used to represent the relationship between entities i.e: people connections in social media, connections between cities, relationship between steps of a data pipelines etc.
There are many types of graph but I would like to highlitght four of them in this post.
- Connected: In this kind of graph you can get from the root to any node.
- Unconnected: This type graph have more than a set of nodes and vertices that are not connected between them.
- Undirected: In this kind of graph vertices do not point to a specific direction, meaning you can transverse from a node to another forward and backward.
- Directed: This type of graph define to which direction the vertices go. It could be forward, backward or both.
There are two ways to represent graph data structure, adjacency list and adjacency matrix. Spoiler Alert: I find the first one easier to implement and understand but I will explain both of them here.
Adjacency List
It is formed by an array of linked list that represent where each index in the array represent nodes in a graph and each node in the linked list represent the vertices connection of the node. Take a look at the following image to have a broad idea of how it will look like.
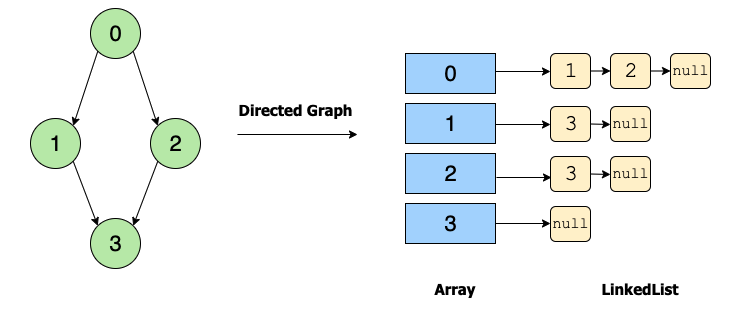 Adjacency List Representation Image by educative.io
Adjacency List Representation Image by educative.io
Here is an example of how adjacency list will look like in Java code:
public class Graph{
private int vertices;
private LinkedList<Integer> adjacencyList[] = new LinkedList<>();
}Adjacency Matrix
It is composed of a two dimensional array of integers where the first row and column represent the nodes in a graph and the internal elements of the array represent vertices. When a connection exits between two nodes the value of the element is set to 1.
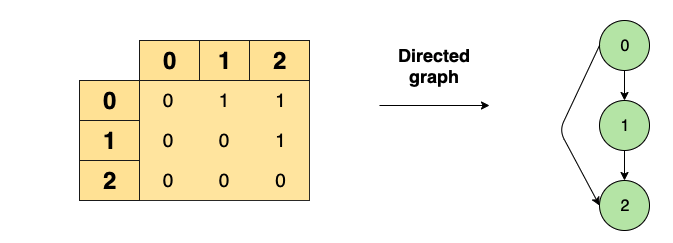 Adjacency Matrix Representation Image by educative.io
Adjacency Matrix Representation Image by educative.io
Here is an example of how adjacency matrix will look like in Java code:
public class Graph{
private int vertices;
private int[][] adjacencyMatrix = new int[vertices][vertices];
}___
In a next post I will explain how to transverse a graph with bread first search and depth first search using both respresentations.